database (DB)
What is a database?
A database is information that is set up for easy access, management and updating. Computer databases typically store aggregations of data records or files that contain information, such as sales transactions, customer data, financials and product information.
Databases are used for storing, maintaining and accessing any sort of data. They collect information on people, places or things. That information is gathered in one place so that it can be observed and analyzed. Databases can be thought of as an organized collection of information.
What are databases used for?
Businesses use data stored in databases to make informed business decisions. Some of the ways organizations use databases include the following:
- Improve business processes. Companies collect data about business processes, such sales, order processing and customer service. They analyze that data to improve these processes, expand their business and grow revenue.
- Keep track of customers. Databases often store information about people, such as customers or users. For example, social media platforms use databases to store user information, such as names, email addresses and user behavior. The data is used to recommend content to users and improve the user experience.
- Secure personal health information. Healthcare providers use databases to securely store personal health data to inform and improve patient care.
- Store personal data. Databases can also be used to store personal information. For example, personal cloud storage is available for individual users to store media, such as photos, in a managed cloud.
Evolution of databases
Databases were first created in the 1960s. These early databases were network models where each record is related to many primary and secondary records. Hierarchical databases were also among the early models. They have tree schemas with a root directory of records linked to several subdirectories.
Relational databases were developed in the 1970s. Object-oriented databases came next in the 1980s. Today, we use Structured Query Language (SQL), NoSQL and cloud databases.
E.F. Codd created the relational database while at IBM. It became the standard for database systems because of its logical schema, or the way it is organized. The use of a logical schema separates the relational database from physical storage.
The relational database, combined with the growth of the internet beginning in the mid-1990s, led to a proliferation of databases. Many business and consumer applications rely on databases.
Types of databases
There are many types of databases. They may be classified according to content type: bibliographic, full text, numeric and images. In computing, databases are often classified based on the organizational approach they use.
Some of the main organizational databases include the following:
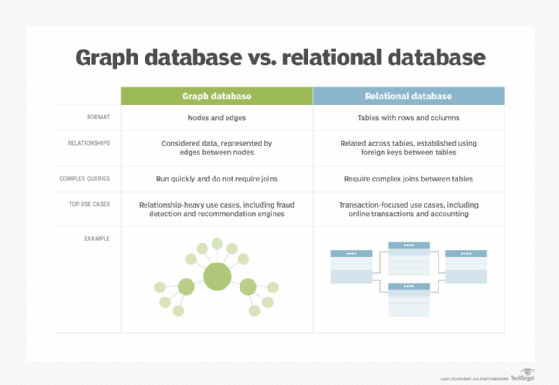
Relational. This tabular approach defines data so it can be reorganized and accessed in many ways. Relational databases are comprised of tables. Data is placed into predefined categories in those tables. Each table has columns with at least one data category, and rows that have a certain data instance for the categories which are defined in the columns. Information in a relational database about a specific customer is organized into rows, columns and tables. These are indexed to make it easier to search using SQL or NoSQL queries.
Relational databases use SQL in their user and application program interfaces. A new data category can easily be added to a relational database without having to change the existing applications. A relational database management system (RDBMS) is used to store, manage, query and retrieve data in a relational database.
Typically, the RDBMS gives users the ability to control read/write access, specify report generation and analyze use. Some databases offer atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability, or ACID, compliance to guarantee that data is consistent and that transactions are complete.
Distributed. This database stores records or files in several physical locations. Data processing is also spread out and replicated across different parts of the network.
Distributed databases can be homogeneous, where all physical locations have the same underlying hardware and run the same operating systems and database applications. They can also be heterogeneous. In those cases, the hardware, OS and database applications can be different in the various locations.
Cloud. These databases are built in a public, private or hybrid cloud for a virtualized environment. Users are charged based on how much storage and bandwidth they use. They also get scalability on demand and high availability. These databases can work with applications deployed as software as a service.
NoSQL. NoSQL databases are good when dealing with large collections of distributed data. They can address big data performance issues better than relational databases. They also do well analyzing large unstructured data sets and data on virtual servers in the cloud. These databases can also be called non-relational databases.
Object-oriented. These databases hold data created using object-oriented programming languages. They focus on organizing objects rather than actions and data rather than logic. For instance, an image data record would be a data object, rather than an alphanumeric value.
Graph. These databases are a type of NoSQL database. They store, map and query relationships using concepts from graph theory. Graph databases are made up of nodes and edges. Nodes are entities and connect the nodes.
These databases are often used to analyze interconnections. Graph databases are often used to analyze data about customers as they interact with a business on webpages and in social media.
Graph databases use SPARQL, a declarative programming language and protocol, for analytics. SPARQL can perform all the analytics that SQL can perform, and can also be used for semantic analysis, or the examination of relationships. This makes it useful for performing analytics on data sets that have both structured and unstructured data. SPARQL lets users perform analytics on information stored in a relational database, as well as friend-of-a-friend relationships, PageRank and shortest path.
What are the components of a database?
While the different types of databases vary in schema, data structure and data types most suited to them, they are all comprised of the same five basic components.
- Hardware. This is the physical device that database software runs on. Database hardware includes computers, servers and hard drives.
- Software. Database software or application gives users control of the database. Database management system (DBMS) software is used to manage and control databases.
- Data. This is the raw information that the database stores. Database administrators organize the data to make it more meaningful.
- Data access language. This is the programming language that controls the database. The programming language and the DBMS must work together. One of the most common database languages is SQL.
- Procedures. These rules determine how the database works and how it handles the data.
What are database challenges?
Setting up, operating and maintaining a database has some common challenges, such as the following:
- Data security is required because data is a valuable business asset. Protecting data stores requires skilled cybersecurity staff, which can be costly.
- Data integrity ensures data is trustworthy. It is not always easy to achieve data integrity because it means restricting access to databases to only those qualified to handle it.
- Database performance requires regular database updates and maintenance. Without the proper support, database functionality can decline as the technology supporting the database changes or as the data it contains changes.
- Database integration can also be difficult. It can involve integrating data sources from varying types of databases and structures into a single database or into data lakes and data warehouses.
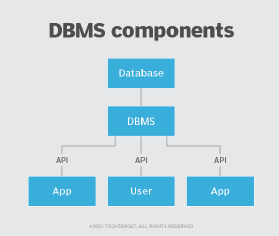
What is a database management system?
A DBMS enables users to create and manage a database. It also helps users create, read, update and delete data in a database, and it assists with logging and auditing functions.
The DBMS provides physical and logical independence from data. Users and applications do not need to know either the physical or logical locations of data. A DBMS can also limit and control access to the database and provide different views of the same database schema to multiple users.
Learn more about the state of data management today and how databases fit in.






