PL/SQL (procedural language extension to Structured Query Language)
In Oracle database management, PL/SQL is a procedural language extension to Structured Query Language (SQL). The purpose of PL/SQL is to combine database language and procedural programming language. The basic unit in PL/SQL is called a block and is made up of three parts: a declarative part, an executable part and an exception-building part.
Because PL/SQL enables users to mix SQL statements with procedural constructs, it is possible to use PL/SQL blocks and subprograms to group SQL statements before sending them to Oracle for execution. Without PL/SQL, Oracle must process SQL statements one at a time. In a network environment, this can affect traffic flow and slow down response time. PL/SQL blocks can be compiled once and stored in executable form to improve response time.
A PL/SQL program that is stored in a database in compiled form and can be called by name is referred to as a stored procedure. A PL/SQL stored procedure that is implicitly started when an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statement is issued against an associated table is called a trigger.
How PL/SQL works
PL/SQL blocks are defined by the keywords DECLARE, BEGIN, EXCEPTION and END, which divide the block into a declarative part, an executable part and an exception-building part, respectively. The declaration section of the block is used to define and initialize constants and variables; if a variable is not initialized, it will default to NULL value. Blocks can be nested and submitted to interactive tools, like SQL*Plus.
PL/SQL is designed to compute and return a single scalar value or a single collection, such as a nested table or VARRAY. Users can create their own functions to supplement those provided by Oracle. While functions can be used in an SQL statement, procedures cannot.
Examples of PL/SQL features
Examples of PL/SQL features include cursors, embedded PL/SQL and calling a stored procedure.
Cursors act as pointers to the context area. A PL/SQL block uses a cursor to control the context area. Cursors can remain unnamed or anonymous, but named cursors make retrieval easier. Cursors can be implicit or explicit. Implicit cursors are the default cursors in PL/SQL blocks. They are created in lieu of an explicit cursor, when PL/SQL encounters a SELECT statement that returns just one row or when data manipulation language statements, like DELETE, INSERT or UPDATE, are encountered. Explicit cursors grant users better control over the context area and should be used with a SELECT statement query that will return more than one row. Both explicit and implicit cursors have the same output, even though their access is different.
PL/SQL can be embedded in high-level host languages, like C. Programming tools, like Pro*COBOL, interpret PL/SQL blocks as single, embedded SQL statements. This enables users to place PL/SQL blocks anywhere in a host program where they might normally place an SQL statement. When embedding PL/SQL blocks into host programs, be sure to declare the variables that will be shared with PL/SQL and bracket the PL/SQL block with the EXEC SQL EXECUTE and END-EXEC keywords, according to Oracle documentation.
After a Java stored procedure has been loaded and published, users can call it. Users can connect to Oracle with the Pro*C program. Once the proper data is entered, the program will automatically assign all row values in the index-by tables to corresponding elements in the host arrays. The program will repeatedly call the procedure and display each batch of data until no more data is found, according to Oracle's PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference Release 2 (9.2).
Advantages of PL/SQL
PL/SQL is compatible with SQL. Because of this tight integration of the two programs, PL/SQL enables users to utilize all SQL data manipulation, cursor control, transaction statements and all other SQL functions, operators and pseudo-columns. Users aren't required to convert between PL/SQL and SQL data types. Additionally, PL/SQL supports both static and dynamic SQL.
PL/SQL enables users to send a block of statements to the database, which significantly reduces traffic between the app and the database. It is also possible to run PL/SQL on any operating system (OS) or platform where Oracle Database runs.
When stored in subprograms, PL/SQL increases scalability by centralizing access processing on the database server. The memory facilities of the shared server enable Oracle Database to support multiple concurrent users on a single node, according to Oracle.
Users can maintain only one copy of a subprogram on the database server instead of multiple copies on each client system. This increases manageability. Many apps can utilize the subprograms, and users can alter them without affecting the apps that use them.
PL/SQL also enables users to create applications that generate webpages directly from the database. This enables users to make their databases available on the web.
PL/SQL Server Pages enable users to develop webpages and are an alternative to coding a stored subprogram that writes the HTML code one line at a time. During development, PL/SQL Server Pages are used as templates, and users can design layouts and write PL/SQL scripts to generate the content.
PL/SQL vs. SQL
Unlike SQL, PL/SQL is completely unique to Oracle, although it isn't an industry standard, as no other product uses it. PL/SQL is similar to nonobject-oriented procedural programming languages, like C or pascal, and its roots trace back to Ada.
SQL and PL/SQL are significantly different programming languages. Although it is limited, SQL enables users to directly interact with a database. Users are able to use SQL to manipulate objects and data, but SQL doesn't include loops or IF/THEN statements. PL/SQL includes all the features of programming languages and integrates easily with SQL.
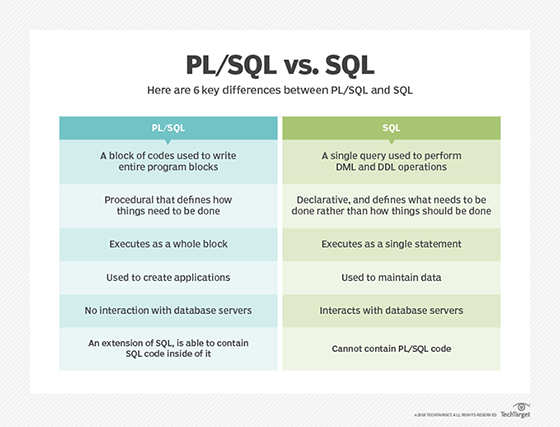
While SQL is considered a source of data for reports, webpages and screens, PL/SQL is viewed as an application language similar to Java and PHP. PL/SQL can be used to build, format and display reports, webpages and screens.






